After the massive success of the Chandrayaan 2 the ISRO now aims at the heart of our solar system the SUN. The next mission of ISRO that is the Aditya L1 mission planned to be executed in 2019-2020 which aims to orbit the sun and observe the corona part of the sun.
What is Aditya L1 mission?
The Aditya-L1 mission was conceived as a 400kg class satellite carrying one payload which was planned to launch in a 800 km low earth orbit. A Satellite placed in the halo orbit around the Lagrangian point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system has the major advantage of continuously viewing the Sun without any occultation/ eclipses. Watch the video below to know more
What is the cost of Aditya L1 mission?
As of July 2019, the mission has an allocated cost of ₹378.53 crore excluding launch costs. Overall the cost may grow to a large extent as launch costs are not considered.Also for this ISRO is planning to do the test launch in Bangalore which may increase the cost.
What are objectives of Aditya L1 mission?
One of the major unsolved issues in the field of solar physics is that the upper atmosphere of the Sun is 1,000,000 K (1,000,000 °C; 1,800,000 °F) hot whereas the lower atmosphere is just 6,000 K (5,730 °C; 10,340 °F).The mission will obtain near simultaneous images of the different layers of the Sun's atmosphere, which reveal the ways in which the energy may be channeled and transferred from one layer to another. Thus the Aditya-L1 mission will enable a comprehensive understanding of the dynamical processes of the Sun and address some of the outstanding problems in solar physics and heliophysics.
- To study dynamic nature of sun's outermost layers , the Corona and the cromosphere and collect data about Coronal Mass ejections(CME)
- Study on the origin of solar storms and their paths through the interplanetary space from the Sun to the earth.
- The studies will also focus on the collection of information for space weather prediction.
Which satellite is used for Aditya L1?
Since the total payload used for the whole project will be around 1500-2000 kilograms so a PSLV XL rocket would be enough to carry all the payloads
Where will the Aditya L1 be placed?
The Aditya L1 satellite is planned to be placed at Lagrange 1 orbit which is in between the orbits of sun and the earth.At these positions will maintain its position relative to large bodies.
What are Lagrange points?
The Lagrangian points or the liberation points or the lagrange points are the points near two large bodies in orbit where a smaller object will maintain its position relative to the large orbiting bodies. At other locations, a small object would go into its own orbit around one of the large bodies, but at the Lagrangian points the gravitational forces of the two large bodies, the centripetal force of orbital motion, and (for certain points) the Coriolis acceleration all match up in a way that cause the small object to maintain a stable or nearly stable position relative to the large bodies.
There are 5 such points available between any two bodies which are labelled L1 to L5.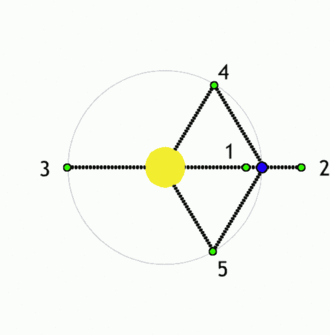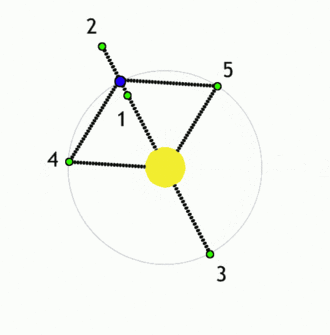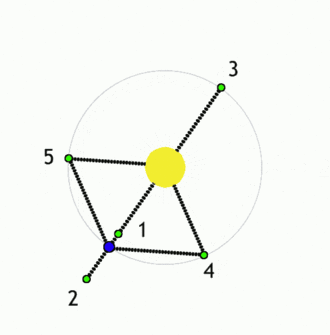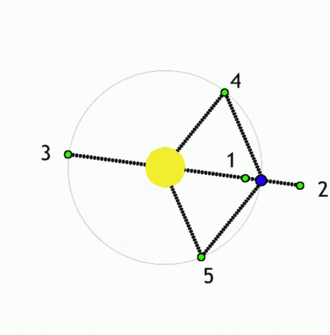
Why the satellite is called Aditya L1?
The five possible lagrange points on earth sun orbit the L1 point is stable and closer to sun. The satellite is designed to operate in the L1 point an since the satellite is designed to operate in L1 point hence it is called Aditya L1 mission. This point is 1.5 million kms away from the earth. At this point the gravitational attraction of sun partially cancels the earth gravitational force.
Partners in Aditya L1 mission?
The mission is not only lead by the ISRO but is also managed by Indian Institute of Astrophysics(Bangaluru),Tata Institute of Fundamental Research(Mumbai) and Inter University for Astronomy and Astrophysics(Pune)
Is Aditya L1 the first satellite to orbit the Sun?
ISRO is not the first space agency to monitor the sun.
The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) which was a NASA and ESA joint venture between USA and Europe which failed due to technical reasons.
The Advanced Composition Explorer(ACE) by NASA is also not much successful due to lack of magnetic field detection hardwares but is still present in the L1 orbit.
Payloads of the Aditya L1 mission.
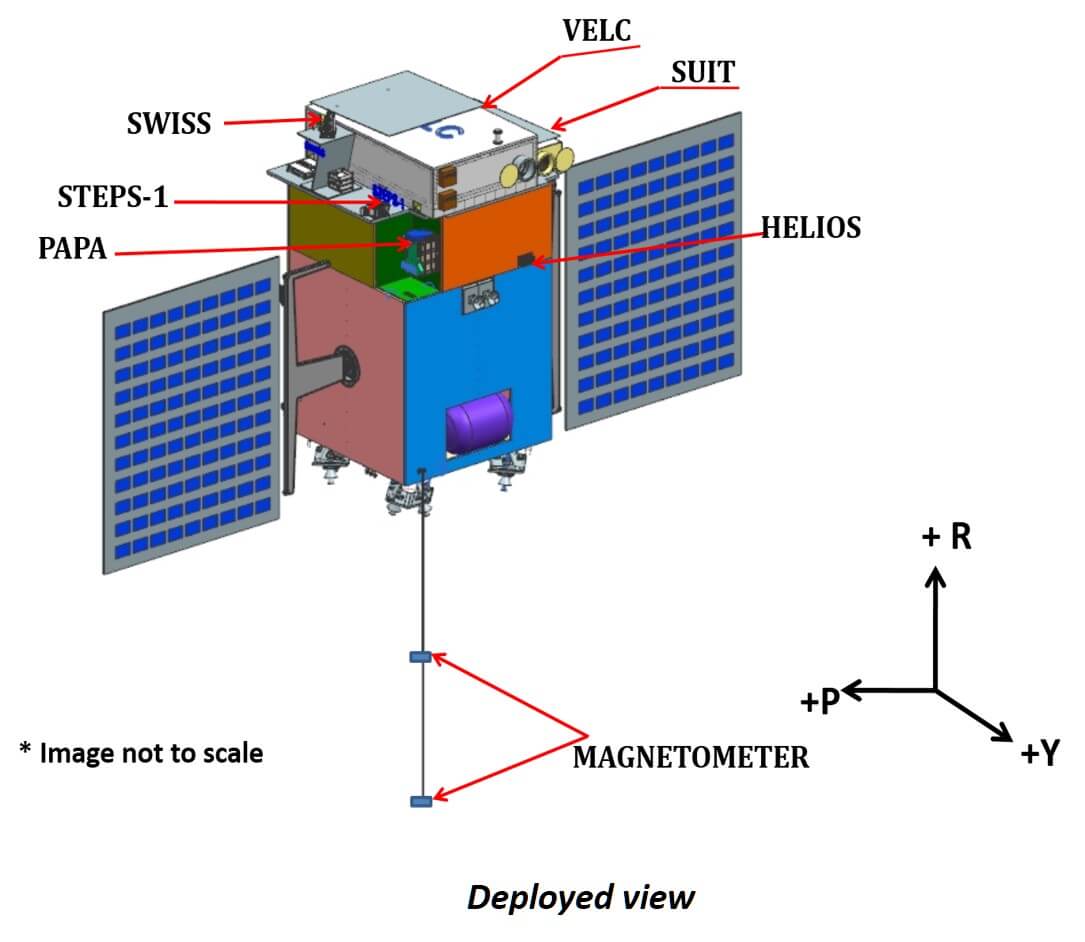
The various payloads used in Aditya L1 missions and their funcions
- Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC): To study the diagnostic parameters of solar corona and dynamics and origin of Coronal Mass Ejections (3 visible and 1 Infra-Red channels); magnetic field measurement of solar corona down to tens of Gauss – Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA).
VELC will address the following science aspects:
• Role of wave in coronal heating
• How are CMEs accelerated ?
• What is the nature of the interaction between the CME plasma and the magnetic field that drives the eruption ?
• What is the configuration of the magnetic field in the corona?
• How are the different components of the solar wind, slow and fast, accelerated ?
• To what degree do coronal inhomogeneities affect the heating and acceleration process ? - Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT): To image the spatially resolved Solar Photosphere and Chromosphere in near Ultraviolet (200-400 nm) and measure solar irradiance variations - Inter-University Centre for Astronomy & Astrophysics (IUCAA)
SUIT will tackle the following issues:
• Coupling and dynamics of the solar atmosphere: What are the processes through which the energy is channelized and transferred from the photosphere to the chromosphere and then to the corona?
• Initiation of CMEs:What are the kinematics of erupting prominences during the early phase?
• Solar irradiance studies:Temporal variation and the spectral variation of the source regions.
• Prominence studies: What are the mechanisms responsible for stability, dynamics and eruption of solar prominences? - Aditya Solar wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX) : To study the variation of solar wind properties as well as its distribution and spectral characteristics – Physical Research Laboratory (PRL)
ASPEX is aimed to:
• Determine the variation of the spectrum of solar wind ions, supra-thermal ions and solar energetic particles during the solar cycle.
• Determine the variation of the thermal anisotropy of the constituents of the solar wind (protons, α-particles, and heavy ions) which is a measure of the efficacy of various acceleration and heating processes thought to occur in the interplanetary medium.
• Study of the supra-thermal tail of solar wind particles and temporal variation.
• Investigate the energy dependence of proton/alpha ratio and the temperature anisotropy of solar wind particles. - Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA) : To understand the composition of solar wind and its energy distribution – Space Physics Laboratory (SPL), VSSC
The goal is to understand the composition of solar wind and its energy distribution. The scientific objectives are:
• Continuous measurement of the solar wind and interplanetary electron distribution functions in the energy range 0.01-3 keV to extract the interplanetary magnetic field structure and topology.
• Study the composition of the solar wind and thereby understanding about the origin of the solar wind and particle acceleration mechanism. - Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS) : To monitor the X-ray flares for studying the heating mechanism of the solar corona – ISRO Satellite Centre (ISAC)
The instrument is being developed at ISAC (ISRO Satellite Center), Bangalore, India. The objective is to monitor the X-ray flares (1-30 keV) for studying the heating mechanism of the solar corona. The payload will provide:
• Data for the study of the DC heating mechanism.
• The physical characteristics of solar flares ranging from the X-class to the A-class along with its association of CMEs.
• Independent measure of coronal temperature and DEM (Differential Emission Measure) as well as abundances of coronal plasma.
• Study of the CME-flare relation and its physical mechanism. - High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS) : To observe the dynamic events in the solar corona and provide an estimate of the energy used to accelerate the particles during the eruptive events - ISRO Satellite Centre (ISAC)and Udaipur Solar Observatory (USO), PRL
The main science goals of HEL1OS are:
• Study of explosive energy release, acceleration and transport of electrons using fast timing measurements and high resolution spectral studies.
• Study of the evolution of low-energy non-thermal electron cut-off using high spectral resolution measurements.
• Provide fast continuous timing data for the study of sub-second variability during flares.
• Understanding the science of eruptive events using complimentary multi-wavelength observations. - Magnetometer : To measure the magnitude and nature of the Interplanetary Magnetic Field – Laboratory for Electro-optic Systems (LEOS) and ISAC.
What question will Aditya L1 solve?
- The temperature of the core of sun is about 5000-6000 Kelvin while the temperature of the corona is about millions of Kelvin.
- This will also solve the twisted magnetic field line of the sun.
- May also help in knowing the origin of sun spots.
Challenges to Aditya L1 program?
- To build a few ultra sensitive instruments to accurately measure minute details about the sun.
- To build a large test center to test the spacecrafts and instruments for the magnetic fields.
- Financial constraints on a developing nation like India
- A prototype will be used to send a satellite to L5 orbit for demo purposes which would need another PSLV launcher.
Chances of success of the mission?
Seeing the past track of ISRO the space agency is expected to be successful in its first attempt making India proud again.